
An article published by the Water Environment Federation in 1969, discussed the idea of using foam fractionation to treat pollution in rivers and other water resources in cities. Foam fractionation is used on a smaller scale whereas continuous foam separation is implemented on a larger scale such as water treatment for a city. Lemlich researched the science behind foam fractionation through theory and equations.Īs stated earlier, continuous foam separation is closely related to foam fractionation where hydrophobic solutes attach to the surfaces of bubbles and rise to form foam. In 1965, Robert Lemlich of the University of Cincinnati made another study on foam fractionation. temperature, position of feed introduction, etc.). Woods in 1964 focused on the various effects of separation based on the changes of certain variables (i.e. studied the effects of pH and concentration on the separation of bovine serum albumin from solution. The earliest documents pertaining to foam separation is dated back to 1959, when Robert Schnepf and Elmer Gaden, Jr.

Protein skimmers are one example of foam separation used in saltwater aquariums. Processes similar to continuous foam separation have been commonly used for decades. Continuous foam separation may not be as efficient in separating solutes as opposed to separating a fixed amount of solution.
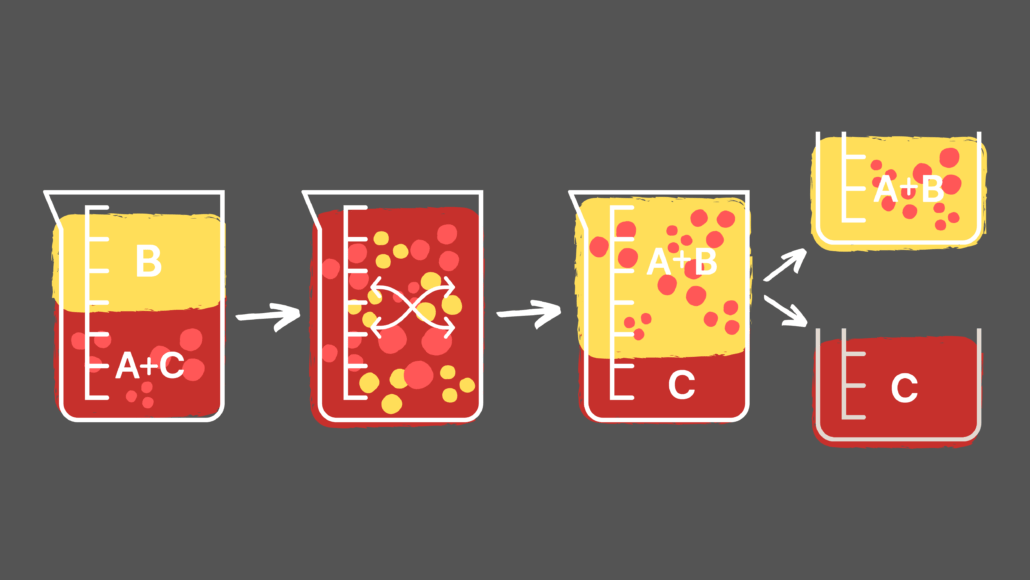
In the continuous foam separation process a continuous gas line is fed into the solution, therefore causing continuous foaming to occur. The foam is then collected and collapsed in another container. A collecting column at the top collects the foam being produced. Air or a specific gas is dispersed in the solution through a sparger. The setup for continuous foam separation consists of securing a column at the top of the container of solution that is to be foamed. As such, what most people usually understand as foam is actually only dry foam. Wet foam forms closer to the originating liquid, while dry foam develops at the outer boundaries. The wet foam is more spherical and viscous, and the dry foam tends to be larger in diameter and less viscous. Wet foam tends to form at the lower portion of the foam column, while dry foam tends to form at the upper portion. They are wet foam (or kugelschaum) and dry foam (or polyederschaum). There are two types of foam that can form from this process. This process is commonly used in large-scale projects such as water waste treatment due to a continuous gas flow in the solution. When a solution is foamed, the most surface active components collect in the foam and the foam can be easily extracted. In any solution, surface active components tend to adsorb to gas-liquid interfaces while surface inactive components stay within the bulk solution. Chemical process in which foam is used to separate components of a solutionĬontinuous foam separation is a chemical process closely related to foam fractionation in which foam is used to separate components of a solution when they differ in surface activity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
